Immigration law serves as the cornerstone of a nation’s regulatory framework, governing the entry, stay, and departure of foreign nationals within its borders. Rooted in the fundamental principles of national security, economic interests, and humanitarian concerns, immigration law plays a pivotal role in shaping a country’s demographics, culture, and socio-economic landscape. This section provides a comprehensive overview of immigration law, delving into its overarching purpose and core principles.
Purpose of Immigration Law
At its core, immigration law is designed to regulate the movement of people across national borders. Nations establish immigration policies to achieve a delicate balance between protecting their interests and promoting global cooperation. The primary purposes of immigration law can be broadly categorized into three main objectives:
National Security
Immigration laws are instrumental in safeguarding a country’s national security. Governments implement stringent entry and exit regulations to prevent potential threats posed by individuals with malicious intent. Through comprehensive background checks, visa screenings, and border controls, nations aim to identify and mitigate security risks, ensuring the safety of their citizens.
Economic Interests
Immigration laws also play a crucial role in addressing a nation’s economic needs. Governments often tailor their immigration policies to attract skilled labor, entrepreneurs, and investors who can contribute to economic growth. Conversely, they may impose restrictions to protect the domestic job market and prevent the exploitation of foreign workers.
Humanitarian Concerns
Humanitarian principles are a significant aspect of immigration law, providing refuge to individuals fleeing persecution, violence, or disaster. Asylum and refugee protections are essential components of these laws, embodying a commitment to human rights and compassion. Striking a balance between humanitarian concerns and national interests remains a continuous challenge for lawmakers.
Core Principles of Immigration Law
The implementation of immigration law is guided by several core principles that underpin its effectiveness and fairness. These principles serve as the foundation for creating a just and balanced immigration system:
Non-discrimination
Immigration laws, ideally, should be free from discrimination based on race, religion, ethnicity, gender, or any other arbitrary factor. Upholding principles of equality ensures that the immigration system is just and promotes diversity within the nation.
Due Process
The concept of due process is integral to immigration law, emphasizing fair treatment and protection of individual rights. Immigrants are entitled to a fair and transparent legal process, including the right to appeal decisions affecting their status, ensuring justice prevails throughout their interactions with the immigration system.
Family Reunification
Many immigration systems prioritize family reunification as a key principle. The recognition of the importance of family ties promotes social cohesion and ensures that families are not unnecessarily separated by immigration policies.
Labor Market Considerations
Immigration laws often consider the needs of the labor market, seeking to balance the demand for specific skills with the available workforce. Policies may be tailored to attract talent that can contribute to economic development while protecting the rights of domestic workers.
In summary, immigration law serves as a multifaceted tool that addresses national security, economic interests, and humanitarian concerns. Its purpose is to strike a delicate balance between maintaining the integrity of a nation and upholding fundamental principles of justice and equality. The core principles of non-discrimination, due process, family reunification, and labor market considerations collectively shape a nation’s approach to immigration, reflecting its values and aspirations. Understanding these fundamentals is essential for fostering informed discussions on immigration policies and their impact on societies worldwide.
Exploring the Landscape of Immigration Law: Different Types of Visas and Their Eligibility Criteria
Immigration law encompasses a vast array of regulations and policies that govern the entry, stay, and exit of individuals from one country to another. One of the key aspects of immigration law revolves around the issuance of visas, which are official documents granting individuals the legal right to enter or reside in a foreign country for a specific purpose. Understanding the various types of immigration visas and their eligibility criteria is crucial for anyone navigating the complex landscape of international mobility.
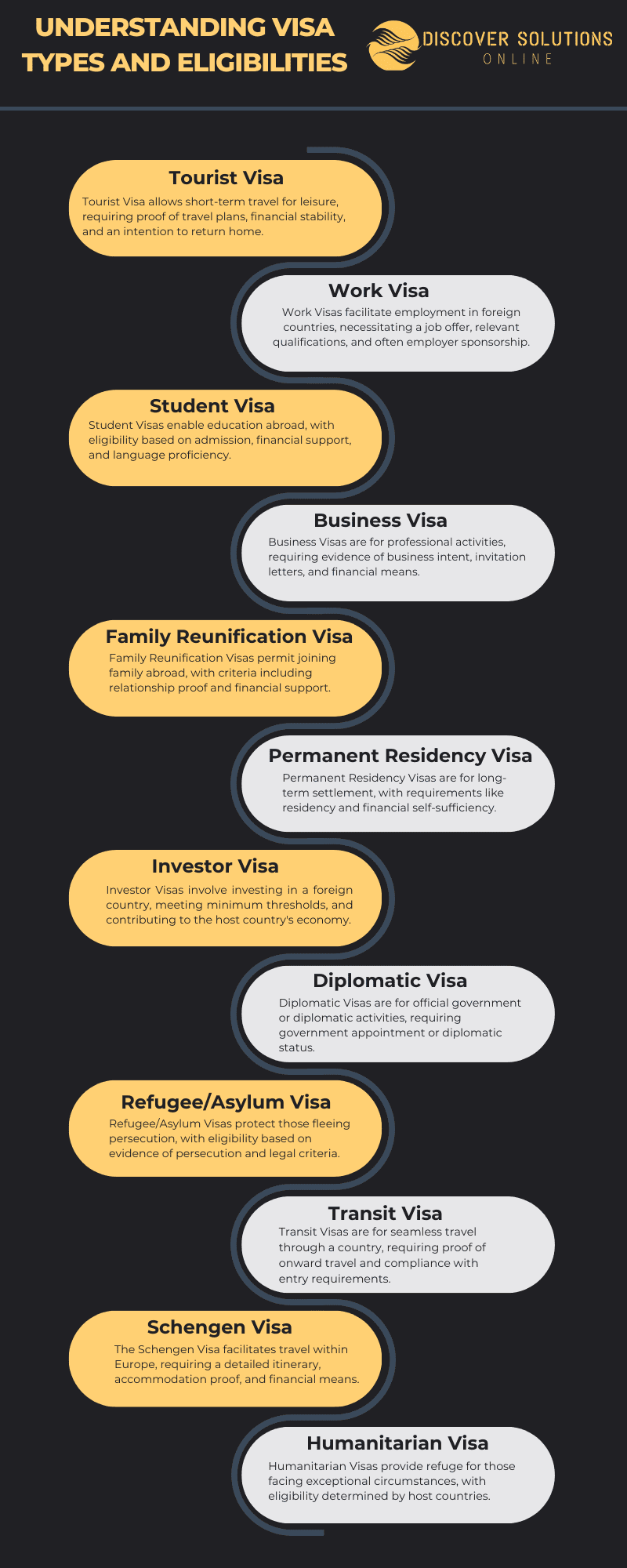
Tourist Visas
Tourist visas are designed for individuals seeking temporary entry into a foreign country for leisure or recreational purposes. These visas typically have a short validity period, and applicants are required to demonstrate their intention to return to their home country after their visit. Eligibility criteria often include proof of financial stability, a round-trip ticket, and accommodation arrangements.
Student Visas
For those aspiring to pursue education abroad, student visas provide the necessary authorization. Eligibility criteria may include an acceptance letter from a recognized educational institution, proof of financial support, and sometimes language proficiency tests. Student visas often allow for part-time employment during the academic term to support living expenses.
Work Visas
Work visas are tailored for individuals intending to engage in employment activities in a foreign country. Eligibility criteria vary depending on the nature of the job, the skills and qualifications of the applicant, and the demand for such skills in the host country. Employers may also play a crucial role in sponsoring and facilitating work visa applications.
Family Reunification Visas
Family reunification visas aim to bring together family members who are separated by international borders. Eligibility criteria often depend on the relationship between the petitioner and the beneficiary, with spouses, children, and parents usually given priority. Applicants may need to prove the genuineness of their relationships and their ability to financially support their family members.
Refugee and Asylum Visas
Designed to offer protection to individuals fleeing persecution, refugee and asylum visas are granted to those who can establish a well-founded fear of persecution based on factors such as race, religion, nationality, political opinion, or membership in a particular social group. The eligibility criteria involve providing evidence of the threat faced in the home country.
Entrepreneur and Investor Visas
Many countries encourage foreign investment and entrepreneurial activities through specialized visas. Eligibility criteria often include a minimum investment threshold, a viable business plan, and the potential to generate employment opportunities in the host country. These visas aim to stimulate economic growth and innovation.
In conclusion, the world of immigration law is diverse, reflecting the myriad reasons individuals seek entry into foreign countries. From tourists and students to skilled workers and refugees, each category of visa serves a specific purpose, and their eligibility criteria are tailored accordingly. Navigating this intricate web of regulations requires a thorough understanding of the nuances involved, ensuring a smoother and legally compliant journey for those seeking to cross international borders.\
The Legal Process of Applying for an Immigration Visa
Immigration law serves as the guiding force behind the movement of individuals across borders, shaping the legal landscape that governs the entry, stay, and eventual citizenship of foreign nationals in a new country. One crucial aspect of immigration law is the intricate process of applying for an immigration visa, a pivotal step for those seeking to establish a new life in a different nation. In this section, we’ll delve into the multifaceted legal procedures involved in obtaining an immigration visa.
Understanding Immigration Visas
An immigration visa is a legal document that grants individuals permission to enter and reside in a foreign country for a specified period. The process of obtaining this visa is often complex and varies from country to country, reflecting the unique policies and priorities of each nation. However, there are common threads that weave through the majority of immigration systems, offering a general roadmap for prospective immigrants.
Identifying the Appropriate Visa Category
The initial step in the immigration visa application process is identifying the most suitable visa category. Countries typically offer various visas tailored to different purposes, such as work, family reunification, education, or asylum. Prospective immigrants must carefully evaluate their circumstances and choose the category that aligns with their intended stay and activities in the host country.
Gathering Required Documentation
Once the visa category is determined, applicants must compile a comprehensive set of documents to support their application. These documents often include proof of identity, financial stability, employment status, educational qualifications, and, in some cases, a clean criminal record. Each country outlines specific requirements, and adherence to these criteria is crucial to the success of the application.
Submitting the Application
With the documentation in order, applicants must submit their visa application to the relevant immigration authorities. Submission methods vary, with many countries now offering online application portals to streamline the process. It is essential to pay close attention to deadlines, submission guidelines, and any applicable fees to ensure a smooth application experience.
Biometric Data Collection and Interviews
In many cases, applicants are required to undergo biometric data collection, which includes fingerprinting and facial recognition scans. Additionally, some countries mandate personal interviews as part of the application process. These interviews serve as an opportunity for immigration officials to assess the applicant’s credibility, intentions, and eligibility for the requested visa.
Waiting Period and Decision
Once the application is submitted, a waiting period ensues during which immigration authorities review the materials and conduct background checks. The duration of this period varies widely and can range from a few weeks to several months. Applicants are advised to remain patient during this phase, as thorough evaluations are conducted to ensure the integrity and security of the immigration process.
Visa Approval or Denial
After the waiting period, applicants receive a decision regarding their visa application. If approved, individuals will be granted a visa with specific conditions, such as the duration of stay, permitted activities, and any additional requirements. In the case of a denial, authorities typically provide reasons for the decision, allowing applicants to address any deficiencies and reapply if necessary.
In conclusion, the legal process of applying for a visa is a comprehensive journey that demands meticulous preparation, adherence to guidelines, and patience. By understanding the key steps involved, prospective immigrants can navigate the complex immigration landscape with greater confidence, paving the way for a successful and legally sound transition to a new life in a foreign land.